Expanding into another state can unlock new markets, tax benefits, and growth opportunities, but it also requires careful planning, compliance, and financial considerations. Understanding state-specific regulations, filing fees, and tax implications ensures a smooth expansion.
Yes, you can open a business in another state by filing a foreign qualification, which costs between $50 and $300 depending on the state. You’ll also need a registered agent in that state, typically costing $100–$150 per year. Other potential expenses include business licenses, sales tax permits, and compliance filings.
In this guide, we’ll cover:
- Foreign qualification costs and requirements in 2025.
- How to maintain compliance and avoid double taxation.
- Step-by-step registration for opening a business in another state.
Let’s dive into the details and help you expand your business seamlessly.
Laying the Foundation for Multi-State Operations
Expanding your operations into multiple states is a strategic move for business owners seeking growth and a broader market. If you're unsure at what point do I need an LLC, evaluating your business growth and liability protection needs is a good starting point. Whether you plan to register your business in a state where you already operate or in an entirely new jurisdiction, understanding the foundation is critical. This process involves evaluating your business structure and ensuring you meet the necessary registration requirements. It also means adapting your articles of organization and articles of incorporation to accommodate new markets. As you prepare to conduct business in multiple locations, consider the impact on your legal entity status, compliance with reporting requirements, and any adjustments to your operating agreement. These factors lay the groundwork for smooth, scalable expansion and help ensure your business remains business friendly while maximizing its tax advantages.
Expand Your Business Seamlessly
ZenBusiness helps you file foreign qualification and manage compliance as you enter new states.
Domestic vs. Foreign Registration: What You Need to Know
When expanding your business, you must choose between domestic registration (forming your business in your home state) and foreign registration (registering as a foreign entity in another state). Domestic registration is often more straightforward if your operations, assets, and physical presence are concentrated in one state. Understanding the benefits of a domestic LLC can help determine whether you need to register as a foreign entity or keep operations centralized. In contrast, foreign registration is required when you plan to conduct business in a state different from where your business is organized. This decision affects your filing fees, annual report obligations, and compliance with state-specific business law. Below is a comparative table to guide your decision:
| Aspect | Domestic Registration | Foreign Registration |
|---|---|---|
| Filing Fees | Generally lower; single state fee | Additional fees per state |
| Compliance Requirements | Fewer; managed under one state's regulations | Must meet multiple states’ reporting requirements |
| Tax Implications | Straightforward income tax filings | May face differing state income taxes and sales tax |
| Legal Process | Simple, well-documented process | Involves certificate of authority and foreign qualification |
Navigating Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
Operating in another state requires a clear understanding of legal and regulatory frameworks to ensure compliance and smooth operations. This means learning about the law in each jurisdiction where you plan to operate, reviewing necessary filing requirements, and ensuring you obtain the appropriate business license and certificate of authority. Understanding these frameworks helps mitigate legal issues and ensures that you can conduct business effectively across state lines.
Understanding Foreign Qualification Requirements
Foreign qualification is the process by which a business registers in a state other than its home state. This is essential if you plan to establish a physical presence or conduct business activities regularly outside your home jurisdiction. In 2025, the process typically involves submitting various documents to the state’s Secretary of State, paying the required filing fees, and meeting specific reporting requirements. These requirements may include an annual report and updates on any changes in your business structure. Completing foreign qualification correctly allows your business to enjoy the tax advantages and legal protections of operating as a registered foreign corporation.
Key Documents and Filing Procedures
When registering as a foreign entity, certain documents are critical:
- Articles of Organization/Amendment: Updated to reflect your multi-state expansion.
- Certificate of Authority: Issued by the state to legally conduct business.
- Operating Agreement: Outlines management and operational procedures.
Before submitting your application, verify that all documents meet the state’s file requirements and registration requirements. If you're wondering how to get an LLC started, ensuring all documentation is correct before filing is crucial for a smooth process. Once gathered, review and file them online or via mail, ensuring that you comply with every aspect of the registration process.
State-Specific Licensing and Compliance Essentials
Each state has its own set of licensing and compliance rules. Reviewing your state's LLC annual fees is crucial to avoid unexpected renewal costs and maintain good standing. For example:
- License Requirements: Obtain a business license if local laws demand it.
- Compliance: Follow state-specific reporting requirements, including annual reports and franchise tax filings.
- Registered Agent: Maintain a registered agent in the state to accept service of process.
It is essential to consult the local government’s website for the latest updates and ensure your documents, such as the articles of incorporation, adhere to state-specific guidelines. This proactive approach minimizes potential legal issues and ensures your business remains compliant.
Legal Considerations When Operating Across State Lines
When expanding operations, legal issues become more complex. You must navigate different corporate laws, understand the implications of double taxation, and determine whether you need to register as a foreign llc or a foreign corporation. These decisions affect your tax law compliance, operating agreement, and service of process arrangements. Additionally, you should assess whether to maintain a holding company structure or form a limited liability partnership to protect your personal assets. Ensuring that you meet all registration requirements and filing fees across states is key to transacting business smoothly and avoiding unnecessary legal complications. For those seeking added privacy, an anonymous compliance LLC may offer an additional layer of security while conducting business in multiple states.
Financial and Tax Strategies for Multi-State Businesses
Expanding your business operations across state lines introduces unique financial and tax challenges. Your business must navigate varying state income taxes, sales tax obligations, and franchise tax requirements, all while maintaining a coherent overall financial strategy. Evaluating these factors is essential for optimizing tax benefits and avoiding double taxation. Understanding the financial implications of transacting business in Texas versus other states is crucial for developing a successful multi-state strategy. Below is a comprehensive cost table summarizing these expenses:
| Cost Component | Estimated Range | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| State Filing Fees | $50 – $300+ | One-Time |
| Registered Agent Services | $100 – $150/year | Annual |
| Annual Franchise/Income Tax | Varies by Revenue | Annual |
| Business License/Permits | $0 – $200+ | Varies by Location |
| Compliance/Reporting Fees | $50 – $100/year | Annual |
Evaluating the Tax Implications of Out-of-State Operations
When operating in multiple states, consider the tax implications carefully. These include:
- Income Tax: Different rates and thresholds across states.
- Sales Tax: Varies by state, affecting pricing and profitability.
- Franchise Tax: Some states levy annual fees based on revenue.
Assessing these factors helps ensure that your overall tax burden is manageable. It is also important to consult with tax professionals to learn about the law and develop strategies that optimize your tax benefits. This proactive approach minimizes surprises during tax season and supports sound business administration.
Cost Analysis: State Fees, Registered Agent Services, and Filing Expenses
When registering your business in a new state, you must consider several costs:
- State Filing Fees: These vary by state; for example, some states charge as little as $50, while others may require up to $300 or more. If you're wondering how much for an LLC, costs can range depending on your chosen state and additional requirements.
- Registered Agent Services: Essential for receiving legal documents; prices typically range from $100 to $150 per year. Many business owners ask, do I need a registered agent for my LLC? In most states, having one is mandatory for compliance and legal correspondence.
- Additional Filing Expenses: These may include name reservation fees, expedited processing fees, and fees for obtaining a certificate of authority.
Additional costs may arise if you decide to hire a professional service to handle your business registration and compliance requirements. A careful review of these costs is vital to avoid unexpected expenses. The following table summarizes a comparative cost analysis:
| Expense Category | Low-End Estimate | High-End Estimate |
|---|---|---|
| State Filing Fee | $50 | $300+ |
| Registered Agent Fee | $100/year | $150/year |
| Name Reservation | $10 | $50 |
| Expedited Processing (if needed) | $25 | $50 |
| Total Estimated Initial Cost | $185 | $550+ |
Thorough planning and cost analysis help ensure that you stay within budget as you expand your business operations.
Strategies to Avoid Double Taxation and Optimize Tax Efficiency
To mitigate the risk of double taxation when operating in multiple states:
- Structure Your Business Appropriately: Consider pass-through taxation options.
- Maintain Accurate Records: Ensure all income taxes and franchise taxes are reported correctly.
- Consult with Tax Professionals: Regular consultations can help identify deductions and tax credits.
By focusing on tax planning and optimizing your operating agreement, you can maximize tax benefits and reduce your overall tax burden, ensuring a more efficient financial strategy for your business. Exploring cheap LLC formation services can help keep startup costs low while ensuring compliance with state regulations.
Practical Steps to Open Your Business in Another State
Opening a business in another state involves a series of well-defined steps that can streamline the expansion process. By following a systematic approach, you can ensure compliance with state-specific requirements and avoid common pitfalls. This guide provides actionable insights and best practices to help you register your business efficiently while keeping costs and legal issues in check.
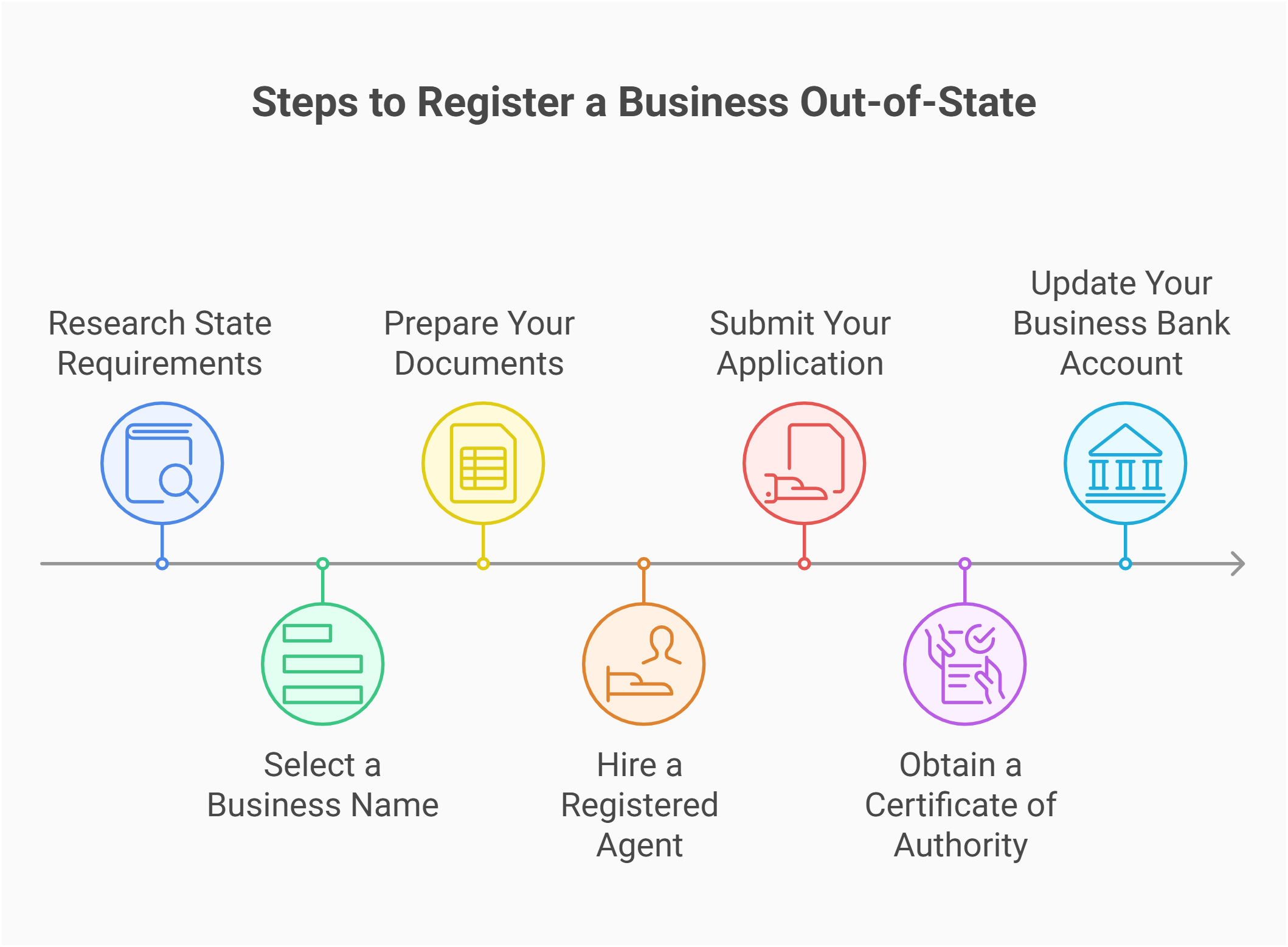
Step-by-Step Guide to Registering Your Business Out-of-State
Expanding your business into a new state requires careful planning and execution. Follow these steps for a successful registration:
- Research State Requirements: Investigate the registration requirements, including filing fees and licensing obligations, on the state's Secretary of State website.
- Select a Business Name: Ensure your chosen name is available and meets the state’s naming guidelines. Consider a name that reflects your brand and complies with both domestic and foreign registration standards.
- Prepare Your Documents: Gather all necessary documents such as articles of organization, an operating agreement, and proof of your home state registration.
- Hire a Registered Agent: Appoint a registered agent in the new state to handle legal documents and service of process.
- Submit Your Application: File your application online or via mail, including payment of the required fees.
- Obtain a Certificate of Authority: Once approved, secure a certificate that permits you to transact business in the state.
- Update Your Business Bank Account: Inform your bank of the new registration to ensure smooth financial operations.
After completing these steps, maintain ongoing compliance by filing annual reports and meeting all local registration requirements. This structured approach ensures you can register your business confidently and expand into new markets seamlessly.
Required Documentation and Best Practices for Filing
When filing to register your business in another state, ensure you have all the necessary documentation:
- Articles of Organization/Amendment: Updated to reflect your expansion.
- Operating Agreement: Clearly details management and ownership.
- Proof of Current Registration: Evidence of your status in your home state.
- Payment Method: Valid credit card or bank information to cover filing fees.
Always double-check the filing requirements for accuracy and completeness, and follow best practices to avoid delays.
Leveraging Technology and Professional Services for Seamless Registration
Utilize online registration portals and professional services to simplify the process. Technology solutions offer step-by-step guidance, real-time status updates, and secure document submission. Additionally, services from legal professionals or registered agent providers can streamline compliance tasks and ensure accuracy. This approach not only saves time but also reduces the risk of errors, making it easier to meet all state-specific requirements while expanding your business efficiently.
Strategic Advantages and Considerations
Expanding your business into another state can offer significant strategic benefits. First, it allows you to tap into new markets, diversify your revenue streams, and gain a competitive advantage by leveraging local market conditions. Second, operating in multiple states may provide tax advantages, such as lower franchise taxes or favorable income tax rates, depending on the region. However, multi-state operations require careful management of legal and financial complexities. Consider factors such as differences in state business regulations, varying reporting requirements, and potential double taxation issues.
- Market Diversification: Enter new markets and reach a broader customer base.
- Tax Efficiency: Optimize tax strategies by choosing states with favorable tax laws.
- Operational Flexibility: Adjust your business structure to meet varying regulatory environments.
- Risk Management: Spread risk across multiple jurisdictions to protect your business assets.
By weighing these factors, you can determine whether expanding your business is the right move. This strategic evaluation will guide your overall business structure and ensure you make informed decisions that support long-term growth.
Stay Compliant in Multiple States
Northwest Registered Agent provides expert guidance on foreign LLC registration and state compliance.
Insights, Case Studies, and Expert Advice
Real-world insights and case studies offer valuable lessons for business owners looking to expand across state lines. This section compiles success stories, common pitfalls, and expert recommendations that can streamline your multi-state registration process and boost your operational efficiency.
Real-World Success Stories of Multi-State Business Owners
Many businesses have successfully expanded by registering in multiple states. For example, a regional retail chain increased its footprint by registering as a foreign entity in neighboring states, leading to a 30% revenue increase. Another case involved a technology startup that leveraged favorable tax rates in several states to reinvest in research and development.
- Retail Expansion: Diversified product lines and targeted local markets.
- Tech Startups: Achieved significant cost savings through strategic tax planning.
- Service Providers: Enhanced customer reach and increased market share by operating in multiple jurisdictions.
These examples underscore the benefits of careful planning and strategic decision-making.
Common Pitfalls and How to Overcome Them
Expanding your business across state lines comes with challenges. Common pitfalls include:
- Incomplete Documentation: Missing required documents can delay registration.
- Underestimating Costs: Hidden fees and varying tax rates may strain your budget.
- Non-compliance: Failing to meet local reporting requirements can result in penalties.
To overcome these issues, thorough research and professional advice are crucial.
Expert Tips for Streamlining Your Multi-State Business Setup
Experts suggest a systematic approach to multi-state business registration. Follow these key tips:
- Plan Thoroughly: Develop a detailed business strategy that covers state-specific regulations.
- Leverage Professional Services: Use registered agent services and legal advisors to ensure compliance.
- Use Technology: Automate document filing and compliance tracking with online platforms.
- Monitor Ongoing Obligations: Stay updated on annual reports, franchise tax filings, and other recurring requirements.
- Review and Optimize: Regularly evaluate your tax strategy and operational processes for efficiency.
By incorporating these strategies, you can streamline your multi-state setup, reduce legal issues, and improve overall operational efficiency. Experts agree that a proactive approach is key to mitigating risks and ensuring sustainable growth.
FAQ: Multi-State Business Registration FAQs
Below is a collection of frequently asked questions to help you navigate the complexities of registering and operating your business in another state. These concise answers provide practical, reliable guidance so you can make informed decisions and expand with confidence.
Yes, you can register your business in another state even if you live in a different state. Many states allow you to register as a foreign entity, provided you meet the registration requirements and designate a registered agent within the state. This process enables you to legally conduct business across state lines while maintaining a primary residence elsewhere. It is essential to review each state’s specific filing fees and compliance obligations to ensure a smooth registration process.
The foreign qualification process involves registering your business as a foreign entity in a state where you do not have your primary place of business. Costs typically include state filing fees, which vary by state, and any additional costs for name reservations or expedited processing. On average, these fees range from $50 to $300, but the total cost may be higher depending on state-specific requirements. Consulting with a registered agent service can also help streamline this process.
Yes, most states require a separate business license or permit for operating within their jurisdiction. Licensing requirements vary by state and industry, so it is important to verify with local authorities what is needed. Additionally, some states mandate annual reports or franchise tax filings, which you must complete to remain in good standing. This ensures that your business complies with all local and state regulations wherever it conducts business.
Managing tax implications across multiple states involves understanding each state’s income tax, sales tax, and franchise tax regulations. To optimize tax efficiency, consult with a tax professional who can advise on strategies to avoid double taxation and leverage any tax advantages available. Keep detailed records of income and expenses in each state, and regularly review your tax obligations to ensure compliance. Utilizing robust accounting software can also help streamline this process.
The documents typically required include your articles of organization or incorporation, an operating agreement, proof of your current business registration, and any necessary state-specific forms. Additionally, you may need to provide a certificate of authority if registering as a foreign entity. Always check with the state’s Secretary of State office or local business registration authority for a complete list of required documents and file requirements before submitting your application.
Simplify Multi-State Business Filings
Harbor Compliance ensures your business meets all legal requirements for smooth expansion into new states.

